Angiogenesis Is Driven by Which of the Following Growth Factors
This is predominantly attributed to the activity of VEGFR-2 following binding of VEGF-A. Under normal physiological conditions most secretory growth factors are associated with components of the extracellular matrix ECM including heparan sulfate proteoglycan and fibronectin 11.

The Angiogenic Cascade During The Process Of Angiogenesis Stable Download Scientific Diagram
Induction of the growth and tube formation of human microvascular endothelial cells through autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor.

. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature by processes of sprouting and splitting. Well known growth factors like platelet derived growth factor PDGF and the granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor GM-CSF have been implicated as endothelial cell growth factors 5354. The developing spout elongates by proliferation of endothelial stalk cells that trail behind the tip cell.
1 Angiogenesis is a highly coordinated tissue-remodeling process activated by proangiogenic growth factors such as VEGF the expression of which is up-regulated in. This study was undertaken to quantify tumor capillaries investigate. Vascular endothelial growth factors are well-known angiogenic agents and targets for anti-cancer therapies.
The growth of new blood vessels is a complex multifactorial process involving the release of several pro- and antiangiogenic factors and different cell types. Angiogenesis the sprouting and growth of new blood vessels from preexisting vasculature is critical for wound healing and in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis diabetes and cancer. VEGF is involved in many steps throughout the fracture healing cascade from initially being concentrated in fracture hematoma to the promotion of bone turnover during the final remodeling phase.
Whether other members of the VEGFR and ligand families such as VEGFR-1 and its ligand Placental Growth Factor PlGF can also contribute to developmental and. The differential expression release and activation of these factors might regulate angiogenesis under various physiological and pathological conditions. Angiogenesis also known as neovascularization is the generation of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature.
Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors and from. Now it appears that this signaling pathway is. Some of these signals such as vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF bind to receptors on the surface of normal.
Capillaries are needed in all tissues. Tip cells navigate toward hypoxic tissue. It occurs throughout life in both health and disease beginning in utero and continuing on through old age.
Signal transduction involves binding to tyrosine kinase receptors and results in endothelial cell proliferation migration and new vessel formation. From angiogenesis to lymphangiogenesis. In the cardiovascular system new blood vessel formation from preexisting vasculature in a process known as angiogenesis is driven by vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF binding to VEGF receptor 2 VEGFR-2 which promotes blood vessel development.
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Advanced glycation end products-driven angiogenesis in vitro.
Advanced glycation end products-driven angiogenesis in vitro. Among the complex system of pro- and antiangiogenic factors the vascular endothelial growth factor system stands out as key mediator of tumor-initiated angiogenesis and as target of antiangiogenesis agents introduced in clinical practice. In the adult a third mechanism called.
The importance of several angiogenic factors has been revealed by gene knockout resulting in embryonic lethality 910. Angiogenesis the sprouting and growth of new blood vessels from preexisting vasculature is critical for wound healing and in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis diabetes and cancer. This process involves the migration growth and differentiation of endothelial cells which line the inside wall of blood vessels.
This process is largely driven by the growth factor vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF whose levels are increased locally and systemically during fracture healing. A number of angiogenic factors including vascular endothelial growth factor basic fibroblast growth factor platelet-derived growth factor angiopoietin-2 and hepatocyte growth factorscatter factor are crucial in glioblastoma angiogenesis. Each binds to transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptors displayed primarily by endothelial cells that are connected to intracellular signaling pathways.
Angiogenesis that is new blood vessel formation is a prerequisite for growth and metastasis of solid tumors. The angiogenic process consists of such multi-steps as degradation of basement membrane cell migration and proliferation and tube formation following activation of vascular endothelial cells by. Angiogenesis one of the hallmarks of cancer has recently become the target of therapeutic approaches in oncology.
Angiogenic activity is induced by growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF basic and acidic FGF and PDGF. It occurs in the embryo from primordial cells vasculogenesis as well as from the sprouting of the preexisting vasculature angiogenesis. No metabolically active tissue in the body is more than a few hundred micrometers from a blood capillary which is formed by the process of angiogenesis.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor VEGFR mediated signalling drives angiogenesis. Transforming growth factor-beta by stimulating target cells to release angiogenic factors or by other mechanisms. The tip cells lead the developing sprout by extending numerous filopodia.
It is a normal process in growth and development and is required for the formation of arteries veins and capillaries in an embryo. Endothelial cells exposed to the highest VEGF-A concentration become tip cells. Angiogenesis is the growth of blood vessels from the existing vasculature.
1 Angiogenesis is a highly coordinated tissue-remodeling process activated by proangiogenic growth factors such as VEGF the expression of which is up-regulated in hypoxic. Vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF is an interesting inducer of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis because it is a highly specific mitogen for endothelial cells. Another group of factors apparently induce angiogenesis indirectly eg.
The process of angiogenesis is controlled by chemical signals in the body. However angiogenic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis diabetic retinopathy solid tumor hemangioma and psoriasis are driven by persistent unregulated angiogenesis. Transdifferentiation to endothelial cells or vascular mimicry has been reported through expression of endothelial markers.
Alternatively it is possible that still other as yet uncharacterized factors play a crucial role in angiogenesis. Up to 10 cash back In addition to production of pro-angiogenic growth factors ECM remodeling enzymes and chemokine signaling macrophages are known to drive angiogenesis through many other mechanisms. Angiogenesis is a complex process in which many growth factors such as VEGF 7 8910 angiopoietin 1 ANG1 basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF among many others are.
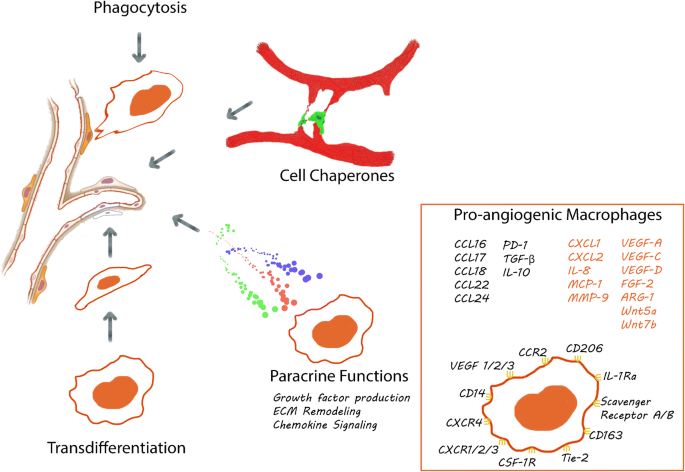
Beyond Growth Factors Macrophage Centric Strategies For Angiogenesis Springerlink

Angiogenesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Promoters And Inhibitors Of Angiogenesis A Balance Of Pro And Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment